Black apricot slowly but surely occupies its niche in orchards located north of the southern regions. The plant is still rare and outlandish, but it may soon become part of the mandatory set of crops that the gardener lays in the planning of the garden. It is worth getting acquainted with the popular varieties of this exotic plant, methods of cultivation and care.
Description of popular varieties of black apricot
Black apricot as a species appeared relatively recently and, interestingly, by accident. As a result of spontaneous pollination of cherry plum and ordinary apricot, a hybrid with fruits of a dark purple (almost black) color is obtained. This fruit was attracted to breeders of different countries by the color, due to which the strange berry began to be popular among buyers. The taste of the berries of the first varieties was mediocre, but the breeders managed to improve it.
Black apricot is sometimes called apricot or plum apricot.
General properties of black apricot varieties:
- Low height. In most varieties, the trees are medium-sized, branched, with a round and spreading crown of medium density.
- Infertility (fruiting begins already in the 2-3rd year).
- High frost resistance of wood and flower buds, which are well resistant to return frosts.
- Late flowering.
- Unpretentiousness to soils and leaving.
- High resistance to fungal diseases and pests.
Among the varieties of black apricot are self-pollinated, partially self-pollinated and self-infertile. All of them are well pollinated by such neighbors as:
- plum;
- cherry plum;
- turn.
Melitopol black
Unlike its counterparts, the tree grows taller - up to 4 m. Due to the larger volume of the crown, it yields high yields - up to 50 kg per tree, which compares favorably with other black apricot varieties.

Melitopol black apricot tree grows up to 4 m
An early ripe variety whose fruits ripen in mid-July. Do not delay in harvesting - ripened berries will not hang on a tree for a long time and will quickly fall off. Fruiting is annual. The fruits are oval, dark red, large. The weight of one reaches 50 g. The taste is excellent, sweet with a honey tint. The pulp is juicy, bright red. The bone separates poorly.
Kuban black
Received in the Krasnodar Territory, entered into the State Register for the North Caucasus Region in 2006. The tree is vigorous, with a thick spreading crown. Unlike other black apricots, it is self-infertile. Pollinators are varieties of cherry plum and plum with matching flowering dates. Kuban black blooms late, berries ripen in late July. Fruiting is irregular. Productivity - 15-20 kg. The berries are oval, laterally compressed, dark purple in color, with a slight pubescence. The mass is small - 25-35 g. The pulp is orange-red, dense, juicy, sweet with acidity, tasty. The stone is medium in size. The purpose is universal, transportability is good.

Apricot berries Kuban black dark purple, with a slight pubescence
Korenevsky black
The crown of this apricot is thickened, therefore, it requires frequent regulatory pruning. The variety has increased demands on the presence of potassium and phosphorus in the soil. With their deficiency, the berries do not ripen. Early maturity - the gardener will see the first fruits in the 3-4th year after planting. Productivity is high, annual. Ripening period is the beginning of August.
The color of the fruit is close to black. The berries are large, round, spherical. With good care, they reach a weight of 60 g. Taste reminiscent of cherry plum, have a pleasant acidity. The flesh is burgundy, juicy, with a pronounced apricot aroma. The bone is small; it separates poorly.

The apricot berries of Korenevsky black have dark maroon, juicy pulp of the taste of cherry plum
Black velvet
Received in the Krasnodar Territory, entered into the State Register in 2006 in the North Caucasus region. The tree typical of most black apricots is medium-sized, with a rounded sprawling, medium-thickened crown. Partially self-fertile variety. It is well pollinated by various varieties of plums, cherry plum, and thorns. The term of entry into bearing is 3-4 years. The average ripening period is in mid-July, the crop is harvested in the southern regions, in the more northern - in early August.
Fruits of circular oval shape, dark purple, weighing 25-35 g, with velvety skin. They have a pleasant, sweet-sour taste with an apricot aroma. The pulp is red, juicy. The bone is small; it separates poorly. Good transportability and shelf life of fruits - slightly unripe berries are stored in a ventilated cellar for up to 4 months.

Apricot berries Black velvet in the southern regions ripen in mid-July
Black Prince
The tree is medium-sized (3-4 m), with a sprawling sparse crown. The variety has early and annual fruiting - the gardener will try the first fruits already in the 2nd year after planting. The black prince is self-fertile, but pollinators will not interfere. Productivity is good, 25-35 kg per tree.
The berries are large (50-80 g), maroon color. Red-orange, juicy and tasty pulp has a sweet and sour taste, not much like apricot, closer to plum and cherry plum.

The fruits of the Black Prince are large, maroon
Video: apricot Black Prince
Planting Black Apricot
Before deciding to plant a black apricot, you must choose a place to plant. It must meet several important criteria:
- Good illumination and ventilation. Black apricot growing in the shade will not bloom and bear fruit.
- Natural protection against cold northerly winds, such as a fence, a building wall or thick trees located north or northeast of the proposed landing site. If this is not possible, you can protect young landings with specially made shields. Painted in white, they will reflect the sun's rays, which will provide additional lighting and heating.
- Moderate soil moisture. Wetlands or areas with a close occurrence of groundwater are categorically unacceptable.
- Loose soil with an acidity of pH 6.5-7 is perfect for planting and growing. On heavy, dense soils, productivity will be low.
- The presence of pollinators near will not be out of place for self-fertile varieties, for the rest it is a prerequisite.
A big plus will be the location of the apricot planting site on the south or southeast slope with a slope of up to 15 °.
The next thing to decide is the choice of landing time. In the southern regions, you can plant both in spring and autumn. In the north - only in the spring. Consider an early spring landing. They choose the time when the sap flow has not yet begun, but nature is already ready for awakening. A young tree, waking up in a new place, will immediately begin to root and by the fall it will get stronger. In this state, it will confidently withstand its first winter.
Seedling selection and storage
This stage will be correctly implemented in the fall:
- Choose and acquire a seedling. It must meet the following requirements:
- Age - 1-2 years. Such seedlings usually have a height of 70-130 cm. More mature ones take root worse, later they bear fruit.
- Well-developed root system, fibrous roots, without growths and cones.

Apricot seedlings should have a well-developed root system with fibrous roots
- The bark is smooth, without cracks and damage.
- On the lower part of the trunk (50-60 cm from the root neck) there should be 3-4 good growth buds or twigs.
- Lay the sapling for winter storage. For this:
- In a basement with an air temperature of 0 ° C to 5 ° C, a wooden box is installed.
- A layer of wet sand is poured onto the bottom of the tank.
- The roots of a seedling are dipped in a mash of clay and mullein, slightly dried and wrapped in a wet burlap.
- The seedling is placed obliquely in a box, the roots are covered with sand and moistened.
- If there is no basement, the seedling is dug in the garden in the same way. In this case, the role of the box will be played by a specially dug hole of a suitable size. After filling the roots with sand, the entire seedling is covered with earth, leaving only the upper part of the branches. They cover it with straw, spruce branches, etc. With the onset of winter, they cover it with snow up to 60 cm thick.
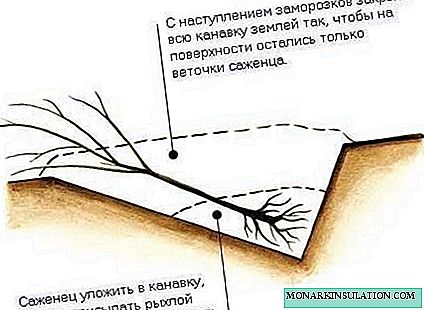
If there is no basement, then the seedling can be dug in the garden until spring.
- In early spring, snow is being raked off. A seedling is taken out just before planting. It should be planted in a sleeping state.
Landing pit preparation
A pit for planting apricot is also prepared in the fall:
- At the chosen place, you should dig a hole with a depth of 70-80 cm with the same diameter. If the top layer is fertile, it is laid aside.

When digging a pit, soddy fertile soil is folded separately
- Prepare a nutrient mixture. You can do this right in the pit by simply mixing the components with a pitchfork or a shovel. The composition includes:
- chernozem (you can use the land set aside when digging);
- humus or compost;
- grass peat;
- sand - these components are taken in equal parts;
- wood ash (1-2 l);
- superphosphate (300-400 g).

The nutrient mixture can be prepared directly in the landing pit
- Cover the pit with roofing material or a film. This protects the nutrients from leaching.
Apricot planting step by step instructions
In due time, they begin the final stage - landing. Act as follows:
- A seedling is taken from the place of winter storage and examined. If everything is okay with him, he wintered well, continue the process.
- Open the pit and, loosening the nutrient mixture, form a small mound. Nearby, at a distance of 10-15 cm from the center, a wooden stake is driven in.
- A sapling is placed on the mound with the root neck to the top, the roots are straightened down.
- They fill the pit and roots with earth, ramming them in layers.

Covering the roots with earth, gently ram each layer
- Check that the root neck is slightly deepened (3-5 cm). It should not be above the surface after watering and shrinkage of the soil.
- The tree is tied to a peg. Do not pinch the barrel too much.
- With the help of a chopper or a plane cutter, a near-trunk circle is formed around the tree.
- Watered with water. This should be done abundantly. As a result, the soil should be well moistened and fit snugly to the roots.

The seedling is watered abundantly
- Mulch with humus, compost, hay or other suitable materials.
- The central conductor is cut to a height of 60-80 cm. If there are branches, they are shortened by a third.
Growing technology
Black apricot in the growing process requires some care, but it is simple.
Watering
It should be remembered that all varieties of black apricot tolerate drought well, but do not like waterlogging. The following irrigation scheme is applied:
- The first watering is carried out in the spring during the flowering period or immediately after its completion.
- The second watering is in early June, when there is a rapid increase in shoots and fruit growth.
- After harvesting, you should water the tree again to restore the forces spent on fruiting.
- In autumn, pre-winter (moisture-charging) irrigation is common for all trees and bushes.
All irrigation should be plentiful, the soil moistened by 30-40 cm. Young trees with a root system that has not yet been developed will need more watering, especially in dry years.
Top dressing
In the landing pit nutrition is laid, which should be enough for 2-3 years. As a rule, apricot is additionally fed after the first harvest.
- In the fall or in the spring, under the digging, organic matter is calculated at the rate of one bucket per 2 m2. This is done once every 3-4 years.
- Also, in spring, nitrogen-containing mineral fertilizers are needed - urea, ammonium nitrate, nitoammofosk, etc. They are introduced annually for digging, after having scattered 30-40 g per 1 m on the surface2.
- For the formation and ripening of fruits in early June, potash fertilizers are needed - potassium monophosphate, potassium sulfate. Dissolve in a bucket of water 10-20 g (this is the norm for 1 m2) and water the trunk circle.
- If the crop is large, you can add liquid fertilizer. To do this, prepare infusions of mullein (2 kg), bird droppings (1 kg) or freshly cut grass (5 kg). The selected base is poured with one bucket of water and insisted for 5-7 days. Then diluted with 1 liter of infusion in a bucket of water and watered. You can do 2-3 such dressings with an interval of 1-2 weeks. 3 weeks before harvesting, top dressing and watering is stopped.
In addition, complex fertilizers containing trace elements can and should be used. When using them, they follow the recommendations given in the instructions. Often they are used as foliar top dressing for spraying trees.
Trimming
Black apricot, like any other, needs to be trimmed:
- Formative pruning. It is important to form an apricot in the first years of life. They finish it, as a rule, by the age of 5-6 years. For trees with a small crown height, a "bowl" shape is more acceptable. It allows you to well illuminate the inside of the crown and greatly facilitates the harvest.

Improved bowl - a good crown shape for black apricot
- Sanitary pruning. It is carried out regularly throughout the life of the plant. Usually in late autumn and (if necessary) in early spring. Dry, diseased and damaged branches are cut out.
- Regulating cropping. It consists in thinning the inner part of the crown by removing the branches growing inside. This should be done in moderation only if the crown is very thickened. We must not forget that the ovaries also form on the inner shoots and the fruits grow. This pruning is usually carried out along with the sanitary.
- Support cropping. Designed to maintain a high level of fruiting. It is carried out in the summer by shortening the annual shoots by 10-15 cm (the so-called chasing). This leads to additional branching and the formation of flower buds. In this way, the crop of the next year is laid.
- Anti-aging pruning. The goal is to extend the life cycle and fruiting of the old tree. It is carried out in two ways:
- The first way is to cut out all the shoots growing from the skeletal branches inside the crown. This causes the growth of new young shoots on which flower buds will form.
- Less commonly used is a method of replacing skeletal branches. This is done in stages, cutting 2-3 branches at a distance of 25-35 cm from the trunk. After this, new shoots grow from sleeping buds. Of these, choose one on each branch located on the outside. He must replace the remote branch. After 2-4 years, the operation can be repeated.
Video: apricot shaping
Crop recommendations
In order not to harm the plant, when conducting pruning, you need to apply simple rules:
- Cut with a sharpened tool.
- Before work, the tool is disinfected with a 1% solution of copper sulfate, hydrogen peroxide, alcohol. It is impossible to use gasoline, kerosene and other petroleum products for these purposes.
- The cutting of branches is carried out "on the ring", hemp should not be left.
- Branches of large diameter are cut in several steps, so as not to damage neighboring ones.
- Slices of branches with a thickness of more than 1 cm are covered with garden varieties.
Experienced gardeners do not recommend using a garden var, which includes refined products (often this is petrolatum). They prefer formulations based on natural components - beeswax, lanolin.
Diseases and Pests
All varieties of black apricot are highly immune to fungal diseases and major pests. An almost complete guarantee of disease avoidance is the regular implementation of a set of sanitary and preventive measures. Therefore, they should not be neglected.
Table: How to Prevent Diseases and Pests
| activity | Duration | Scope of work |
| Collection and disposal of fallen leaves | Autumn | Leaves and cut branches burn. The resulting ash is collected for use as fertilizer. |
| Sanitary pruning | Late fall | |
| Digging soil | Late fall | It is necessary to dig the earth with a revolution of layers. At the same time, wintering pests will be raised to the surface and may die from frost. |
| Inspection and cleaning of the bark | Autumn | Inspect the bark of a tree, if cracks are found, they are cleaned to healthy tissues, disinfected with a 1% solution of copper sulfate and covered with garden var. |
| Whitewashing trunks and branches | Autumn | It is carried out with a solution of slaked lime with the addition of 1% copper sulfate. Prevents sunburn of the bark and prevents the movement of insects. |
| Spraying with 3% solution of copper sulfate | Fall spring | Can be replaced with a 3% solution of Bordeaux fluid or 5% solution of iron sulfate. |
| Shelter of young trees from frost | Late fall | It is convenient to do this with the help of a frame made of wooden blocks, poles or plastic pipes. The frame is fitted with polyethylene or spanbond. |
| Protecting tree trunks from hares | Autumn | Apply roofing material, old linoleum or other improvised materials, wrapping tree trunks. |
| Installation of hunting belts | Early spring | For the manufacture of such materials can be used at hand, such as film, roofing felt, etc. |
| Treatment with complex preparations for fungi and insects | Early spring | Apply:
|
| Systemic fungicide treatments | After flowering and before fruit ripening with an interval of 2-3 weeks | You can use various drugs (preferably biological). Closer to harvest, drugs with a short waiting period are used. For instance:
|
The main diseases of apricot
Apricot is most often infected with fungal diseases:
- kleasterosporiosis. The spores of the fungus that have fallen on the leaves germinate and form small dots of brown or reddish-brown color on the surface. As the dots increase, they turn into spots. If the humidity is high, the process proceeds violently. Over 10-15 days, the size of the spots reaches 5-10 mm, the inner part dries and gets enough sleep, holes form;
- moniliosis. The spores of this fungus bring bees on their paws along with pollen when collecting nectar. Therefore, the flowers suffer first, followed by shoots and leaves. The affected parts fade, sag, as if scorched by a flame;
- cytosporosis. It occurs in the presence of untreated wounds and cracks. Propagating, the fungus causes the destruction of the cortex, which, in turn, provokes gumming. The treatment comes down to cleaning the damaged areas to healthy bark and wood, treating the wound with 1% solution of copper sulfate and antifungal drugs.
Photo gallery: what apricot can get sick

- Over 10-15 days, the size of the spots reaches 5-10 mm, the inner part dries up and gets enough sleep, holes form

- Multiplying, the fungus of cytosporosis causes destruction of the cortex

- Affected parts fade, sag, as if scorched by a flame
Apricot Pests
Apricot can also be attacked by pests.
Weevils
Weevils (small bugs with a long proboscis) winter in cracks of the bark, fallen leaves and upper layers of the soil. During autumn preventive measures, the vast majority of these insects will be destroyed. The survivors, having awakened from hibernation, will climb the trunk (if they do not stop the hunting belt) to the crown. There they begin to satisfy their hunger by eating buds, buds, leaves, shoots, and ovaries. In the early stage, when spring has not yet fully taken over, and in the mornings it is still cool, and the air has not warmed above 5 ° C, you need to go into the garden, spread a cloth or film under the apricot tree and simply shake off the branches of weevils sitting on them .

Weevils - small, beautiful bugs with a long proboscis
Treatment with DNOC or Nitrafen, planned for this time in preventive measures, should completely relieve the gardener of annoying guests.
Khrushchev
In addition to weevils, many different beetles swarm around garden and garden plots - April, May and others. All of them, having satiated with the first young greens, begin to lay eggs in the soil, from which larvae creep out in early June - they are called Khrushchev. In the weevil they are small - 4-6 mm, in the May beetle - 20-25 mm, the largest - in April - reach a length of 35 mm. These larvae feed on plant roots. Khrushchev for young apricots is a great danger. You can fight them using the drug Diazinon (cultivating the soil according to the instructions). For 20 days of action, he will cause irreparable damage to the pest colony. It does not accumulate in soil and fruits.

For the roots of a young apricot, dangers are very dangerous.
Aphid
Aphids are a frequent visitor in gardens. Although there are many more tasty plants on the site, sometimes it does not disdain apricot. You can find it by folded leaves. If you expand them, you can see many small insects of black, green, white and other colors, depending on the type of aphid. It can eat not only leaves, but also young shoots. The struggle consists in the mechanical collection of twisted leaves, followed by treatment with insecticides, for example, Decis, Fufanon.

Aphids can eat not only leaves, but also young shoots
Reviews
Since 2006, I have been growing apricot cultivar "Melitopol black." Here are his fruits in the hands of his daughter (see photo). What can I say: I formed it initially by a small tree by means of strong pruning, but the tree is still weak-growing and does not need pruning, much less shaping, it is very sensitive (at the level of peaches) to any sores, especially to kleasterosporiosis. I process as well as peaches. Low-yielding. But the fruits are very tasty !!! Fruits regularly (every year). In our family there is a constant struggle for the harvest: the husband and daughter like dense, not fully ripened fruits (sour), my son and I like ripe and sweet. When overripening, the fruits are prone to shedding, but the taste of such overripe fruits is honey, the density of the fruit does not suffer (they remain transportable, my garden is covered with a grassy lawn, the fruits remain without damage during shedding). Taste is something between the taste of apricot and plum. Fruits are larger in size than the largest apricots (average between apricot and peach). Ripen much later than apricots, during the period of mass fruiting of plums. The pulp is red or yellow-red, non-fibrous, the bone does not separate, the skin is downy, like an apricot. The fruits ripen at the same time, the ripening period is extended by 2-3 weeks. They didn’t try to cook anything from the fruits (such as compotes and preserves), because eaten at an extremely high speed directly from the tree. And the guests know when exactly this apricot ripens and come to visit to enjoy the fruits.
Irina Kiseleva, Kharkov
//forum.vinograd.info/showthread.php?t=11252
Well, this year I tried the first outlandish apricots. Loved the taste, somewhat reminiscent of a peach. The fruits are quite large, I did not even expect such a size.
Svetlana, Kiev
//forum.cvetnichki.com.ua/viewtopic.php?t=743&p=44955
Black apricot has undoubted advantages and deserves the attention of gardeners. If the first varieties are far from perfect, now the gardener already has plenty to choose from. Unpretentiousness and ease of care bribe, allowing even a novice to grow an unusual berry.





















